What is RAG?
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It is an approach to language modeling where the model retrieves relevant information from an external knowledge source to help inform its generations. The key components are:
- A retriever that finds relevant documents/passages from a knowledge corpus.
- A generator (language model) that incorporates the retrieved information to produce the final output.
Quick filter: If you can’t tell whether the failure is retrieval or reasoning, you can’t fix it yet.
Some benefits of RAG include:
- Context expansion - Allows the model to draw upon a large domain-specific knowledge base instead of relying solely on its parameters.
- Reduced hallucinations - The retrieved contexts provide factual grounding and reduce hallucinations.
- Better explainability - It's easier to isolate why a certain answer was produced and provide citations.
Measuring RAG Performance
When developing and deploying RAG systems, it's critical to measure the performance of both the retriever and end-to-end system:
End-to-end Metrics
These are domain-specific metrics that measure the end-to-end system performance. i.e., is the final answer good?
| Metric | What it measures | Use it to decide |
|---|---|---|
| Factual accuracy | Grounding to trusted sources | If answers match reality |
| Style | Tone and readability | If output fits the audience |
| Conciseness | Signal-to-noise | If responses are too long |
| Toxicity | Unsafe or harmful content | If outputs need filtering |
Hamming includes the following end-to-end metrics by default:
- Factual Accuracy - Measures how well the generated text aligns with established facts and information from reliable sources.
- Style - Evaluate the fluency, coherence, and appropriateness of the generated text for the intended audience and purpose.
- Conciseness - Assesses how well the model conveys information efficiently, avoiding unnecessary repetition or irrelevant details.
- Toxicity - Checks the generated text for inappropriate, offensive, or harmful content that could negatively impact users.
The key is making an AI judge aligned with your definition of good. “Good” is different for a support bot vs. a medical assistant.
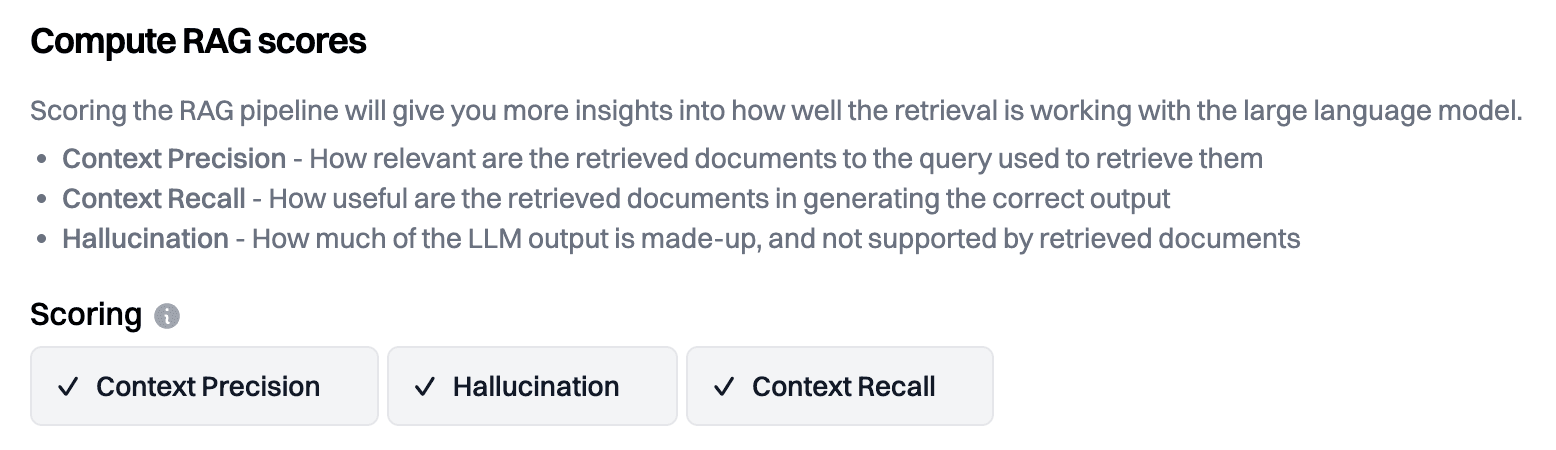
Retrieval Metrics
The following scores measure the quality of the retrieved contexts. i.e., were the retrieved documents 'good'?
- Precision - The % of retrieved documents relevant to the user input. Helpful in measuring signal/noise ratio.
- Recall - The % of statements from the golden output for a given input that are contained in the contexts. If recall is low, no prompt tweaking will improve the answer; the key is to improve the retrieval pipeline through better chunking and search parameters. This is the #1 trap we see.
- Hallucination - Similar to recall. The % of statements from the AI output attributable to the retrieved contexts.
RAG Debugging Pro-Tips
Here's how we think you should debug your RAG pipeline:
Step 1: Run evals on the end-to-end output
The goal here is to isolate specific examples that are underperforming. Debugging averages is a slow way to learn.
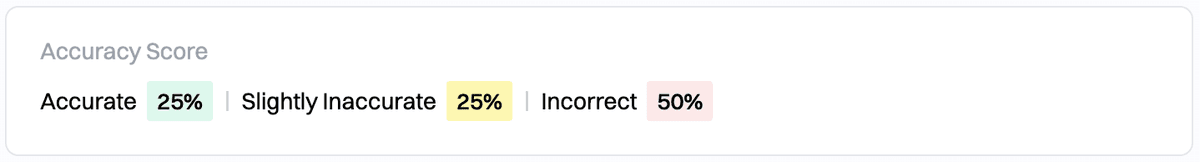
Step 2: Isolate between reasoning and retrieval errors
Use the retrieval metrics to help you differentiate between retrieval errors and reasoning errors.
With Hamming, you can run one-off scores. This is more cost-efficient than running retrieval scores on all cases.
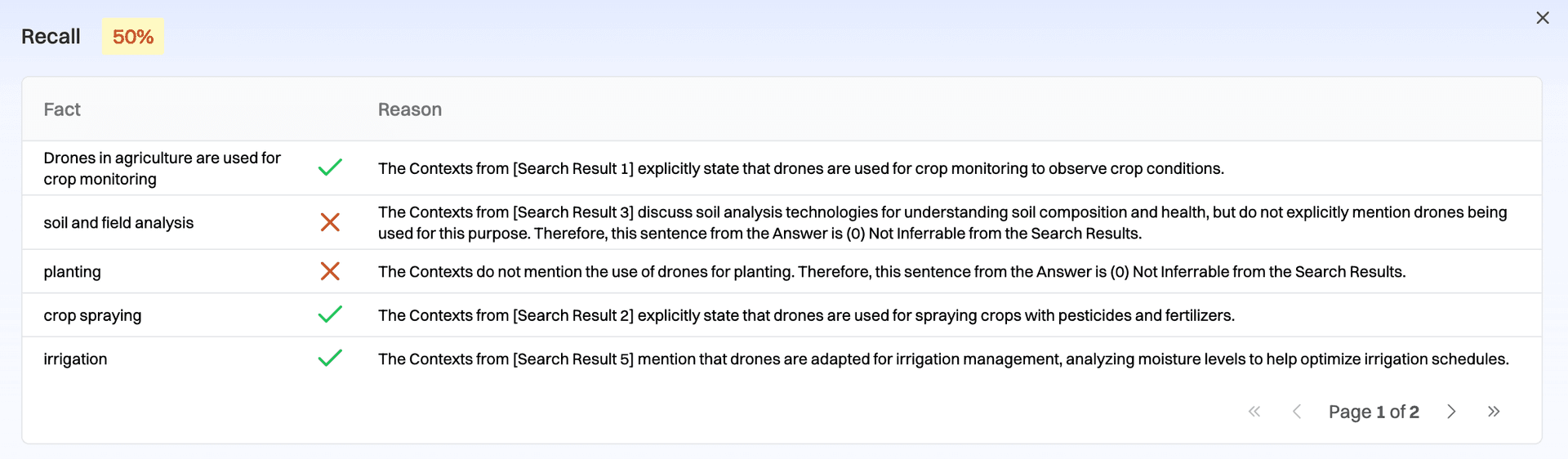
Step 3: If retrieval is the issue
If recall is low, you likely have a retrieval issue. Focus on improving your indexing and retrieval pipeline.

Step 4: If reasoning is the issue
If precision and recall are high, but hallucination is also high, you likely have reasoning errors. Sometimes retrieval can be high, but precision can be low, leading to reasoning errors. The next best move is iterating on the prompts or using a smarter model.


Step 5: Make the necessary changes
Make updates to your prompts or retrieval pipeline to solve for retrieval and reasoning errors.
Step 6: Re-test
Run evals on the end-to-end output to make sure you're improving. It's common to experience regressions after making a small change to your AI pipeline.
Some people believe you can do label-free evaluations of just the retrieval pipeline. In our experience, checking the end-to-end quality first and THEN measuring retrieval performance is more useful. This correlates more with how a user measures quality.

